Stackup uses the onchain state of your smart account as the single source of truth. We recommend following this guide during wallet creation and all subsequent access updates to independently verify the state of your account matches expectations.
Techincal knowledge required
This guide is intended for technical users who are familiar with querying blockchain data and running scripts on a terminal.
1. Export your onchain configuration
All wallet’s onchain configuration can be exported via the Stackup dashboard under the wallet settings.
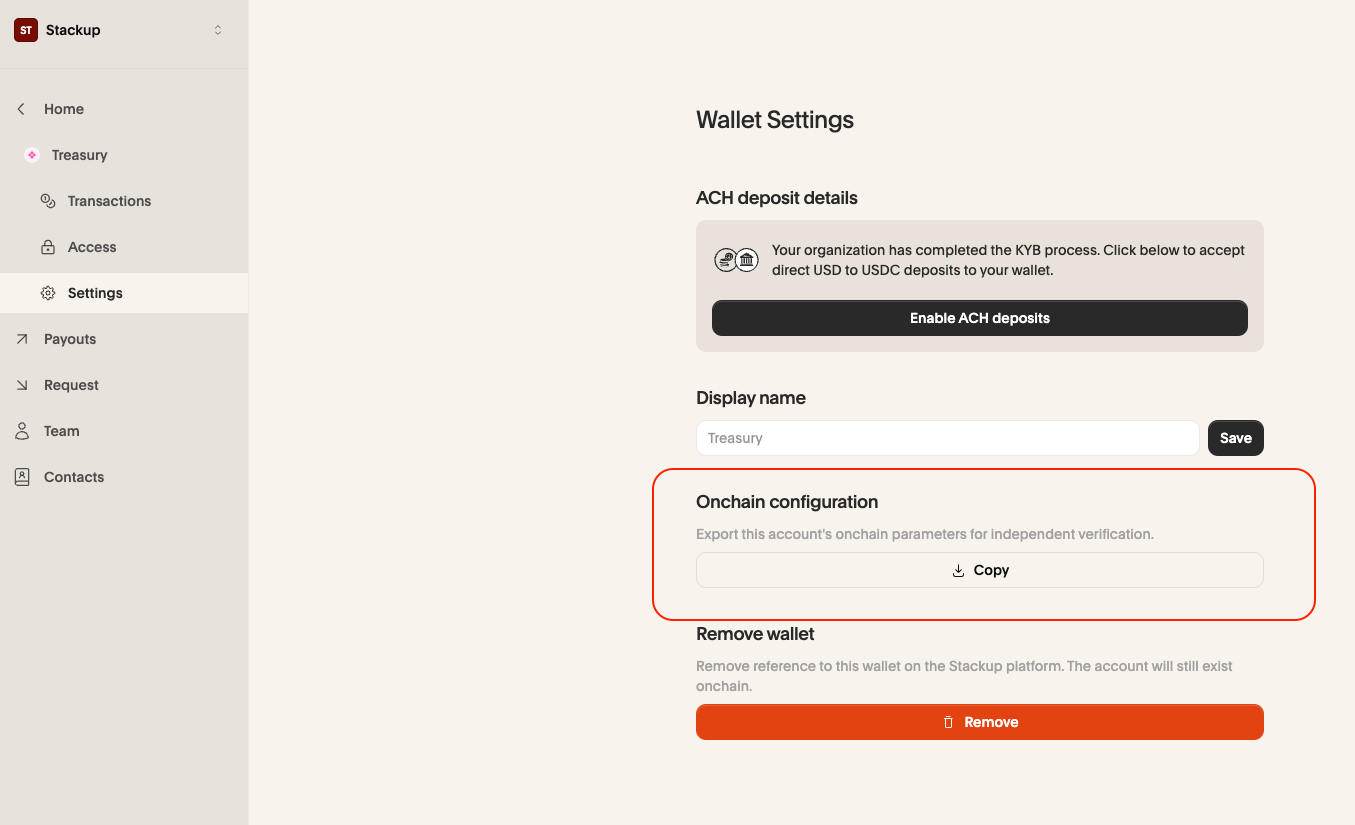
Clicking the “copy” button will result in a JSON with the following data structure being copied to your clipboard.
{
"account": {
"address": "0xC008B9B56a1a7C68E25A4873bEBBEC6D37359964"
},
"factory": {
"address": "0x625cF8EDec3f68d48D3aA385F356524B04760BE8",
"data": "0xd7eb8e818cf3485252207fa8de15de1377884c8bca5415e6dbdcce098f4a36496d9649e02b7c09135a0ff072be9241d3dcec4ac99e727c58d429c2f9f7eea1f01508fe66"
},
"entryPoint": {
"address": "0x4337084D9E255Ff0702461CF8895CE9E3b5Ff108",
"version": "0.8"
},
"keystore": {
"address": "0x69C9F626b5Bd934C0F9806346682eD407FB978d3",
"refHash": "0x8cf3485252207fa8de15de1377884c8bca5415e6dbdcce098f4a36496d9649e0",
"latest": {
"rootHash": "0xfef609a4f739ea279b309b41da8541424689b2374cc215e4f2a2f283ab61412c",
"userConfigurationMerkleTree": [
[
"0xE19620169A26aEbC4Fe229A073639da6b009bF1a",
"0x6f835026f13d3726dcea6946bf58487818b10e501135b5d6e532ebc884904818e92edde1d15c106e03f4e995c7c4e367228020db4b9828ffcb10b60c10b5d8cb"
],
[
"0x939C10DCdA11A73eCCc563340aBE3d257859dC6d",
"0x000000000000000000000000e10980d4bbf1ce70e4767128577902fa3c126b86dbfd06ad5ec165db091035ef00bb60ea920c629ed64e4faf0dd68ca7c63c07e3b7904d1ceb578d498a6069d7b1e6574241af040e93465792f33cd16b9675b410"
],
[
"0x939C10DCdA11A73eCCc563340aBE3d257859dC6d",
"0x000000000000000000000000e10980d4bbf1ce70e4767128577902fa3c126b86698621fc22457ceb7a17bb6d6e618ea7c9f0c29f93a3fc51c19c73b45ef6ca5b9a99111c035689a9f1c566b95c42c11629b02901896637e426d0c6fca25b4ce6"
]
]
}
}
}This might seems a intimidating at first, but lets walk through it.
2. Verifying your account address
Stackup smart accounts are built on v0.8 of the ERC-4337 EntryPoint. First thing we need to do is ensure we are using the canonical address. The entryPoint.version should be 0.8 and the entryPoint.address should be 0x4337084D9E255Ff0702461CF8895CE9E3b5Ff108 as defined in the official release notes.
We also want to make sure that the smart account is being deployed from the canonical keystore account factory. The factory.address should be 0x625cF8EDec3f68d48D3aA385F356524B04760BE8 and the factory.data should be a concatenation of 0xd7eb8e81 (the function selector for createAccount), the 32 byte reference hash (more on this later), and a 32 byte salt.
Lastly, account.address is the address of your onchain smart account that is the same on all EVM blockchains. Rather than trusting this value, we can verify it quiet easily with independent tools like Tenderly.
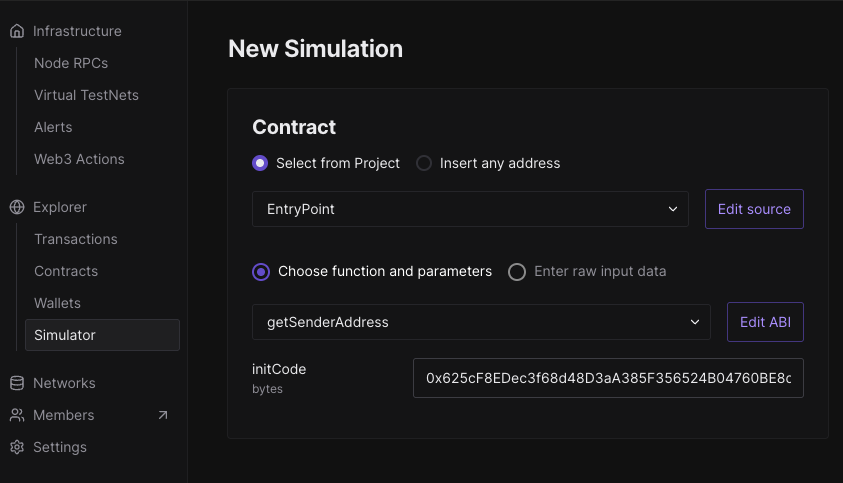
In the Tenderly simulator, we are making a call to getSenderAddress on the v0.8 EntryPoint and setting the initCode as the concatenation of the factory.address and factory.data from our JSON. By design, this call always reverts since it is intended for use during simulations only.
By parsing the CALL output or revert error data, we can see the deterministic sender address that is generated.
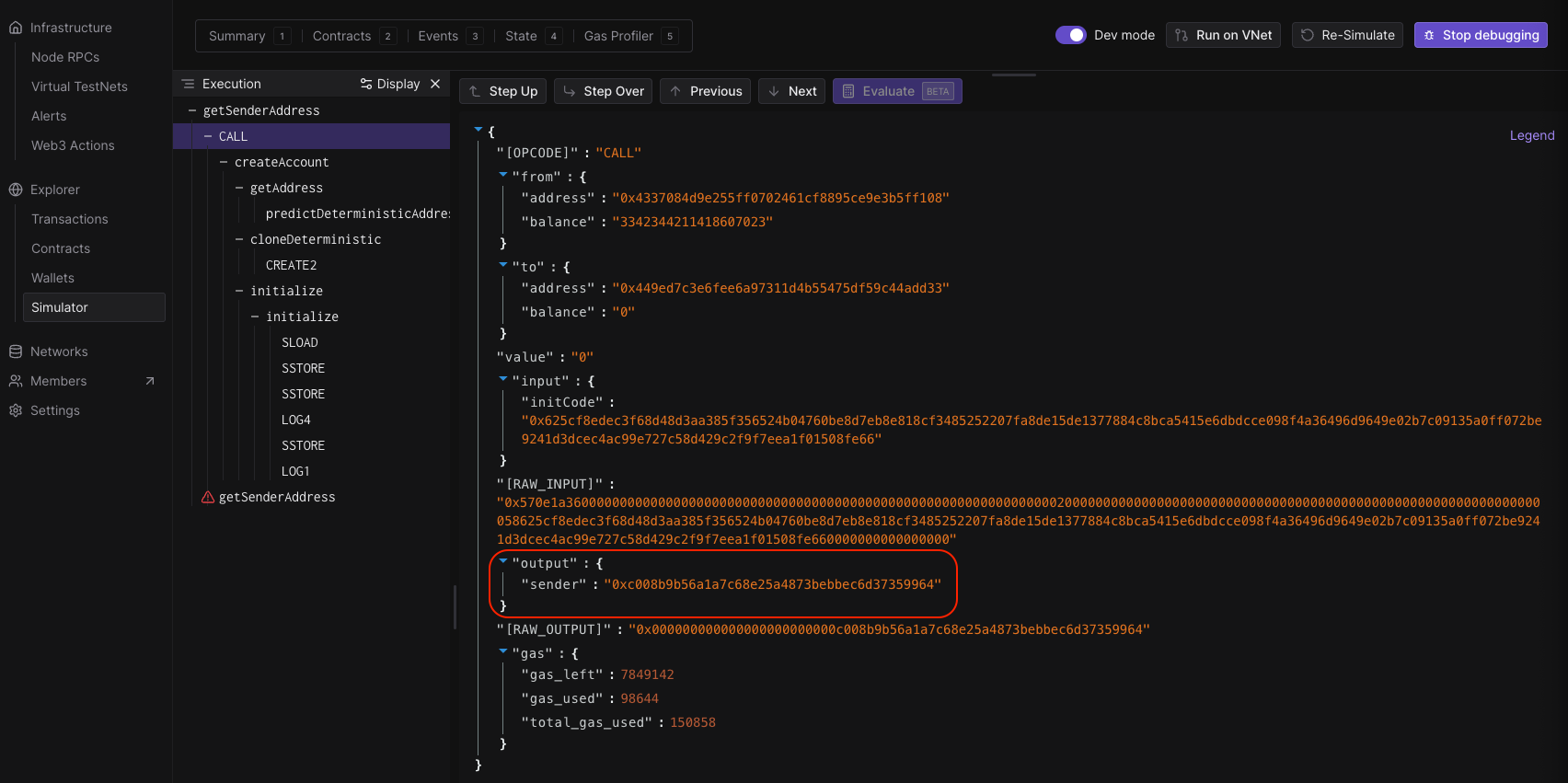
The sender address from the simulation should match your account address which gives strong guarantees that your smart account is in fact using the correct EntryPoint and factory.
3. Verify your access configuration
The last thing we need to do is verify that your access controls are configured with the exact combination of signers you expected. This process also gives cryptographic guarantees that no malicious signers are hiding within your configuration.
First we need to make sure that keystore.address is pointing to the canonical keystore contract at 0x69C9F626b5Bd934C0F9806346682eD407FB978d3. We can then use an independent tool like Etherscan along with the keystore.refHash and account.address value to get our current root hash.
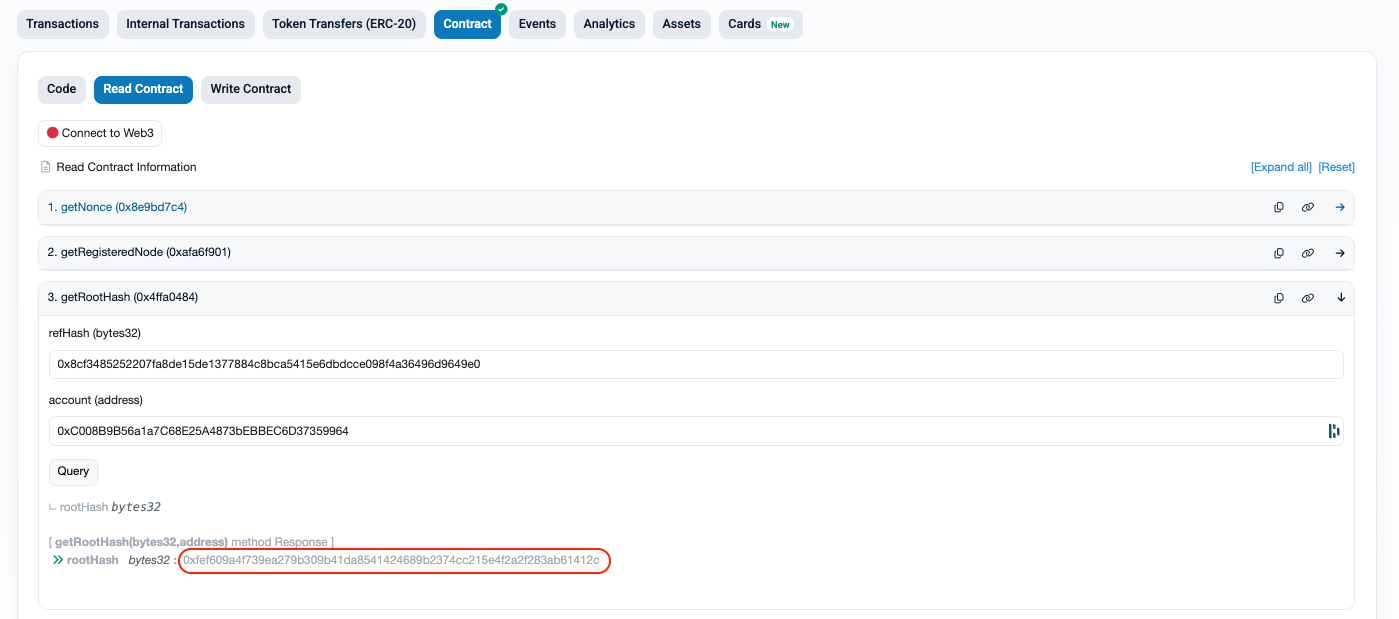
The returned root hash value should match exactly with the value in our JSON keystore.latest.rootHash field. This root hash represents a unique Merkel tree setup and is essential in proving if a signer does or does not belong to your smart account.
The actual Merkel tree configuration can be seen in our JSON keystore.latest.userConfigurationMerkelTree field. This data structure is organized as an array of nodes where each node is a tuple of the verifier address and associated configuration.
0xE19620169A26aEbC4Fe229A073639da6b009bF1arefers to the WebAuthn verifier and the data is a passkey public key. These are used for admins.0x939C10DCdA11A73eCCc563340aBE3d257859dC6drefers to the WebAuthn + ECDSA cosign verifier where the data includes the passkey public key and the cosigner’s ECDSA address. These are used for restricted signers.
In order to prove that this access configuration is complete and accurate, we need to calculate the root hash of the Merkle tree and verify that it matches what we are seeing onchain. We can do this using a open source script from the official keystore repository.
After cloning and installing the dependancies, open the file at examples/verify-ucmt.ts. Replace the current USER_CONFIGURATION_MERKLE_TREE with the value from our JSON.
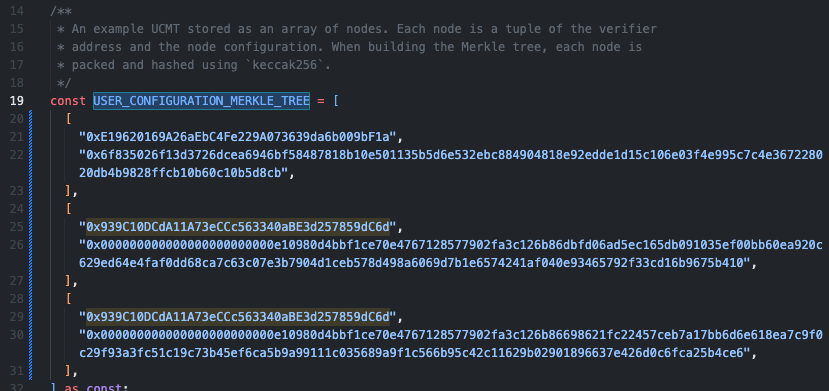
Save the file and run the following command in your terminal.
npm run examples:verify-ucmtYou should see the following output.
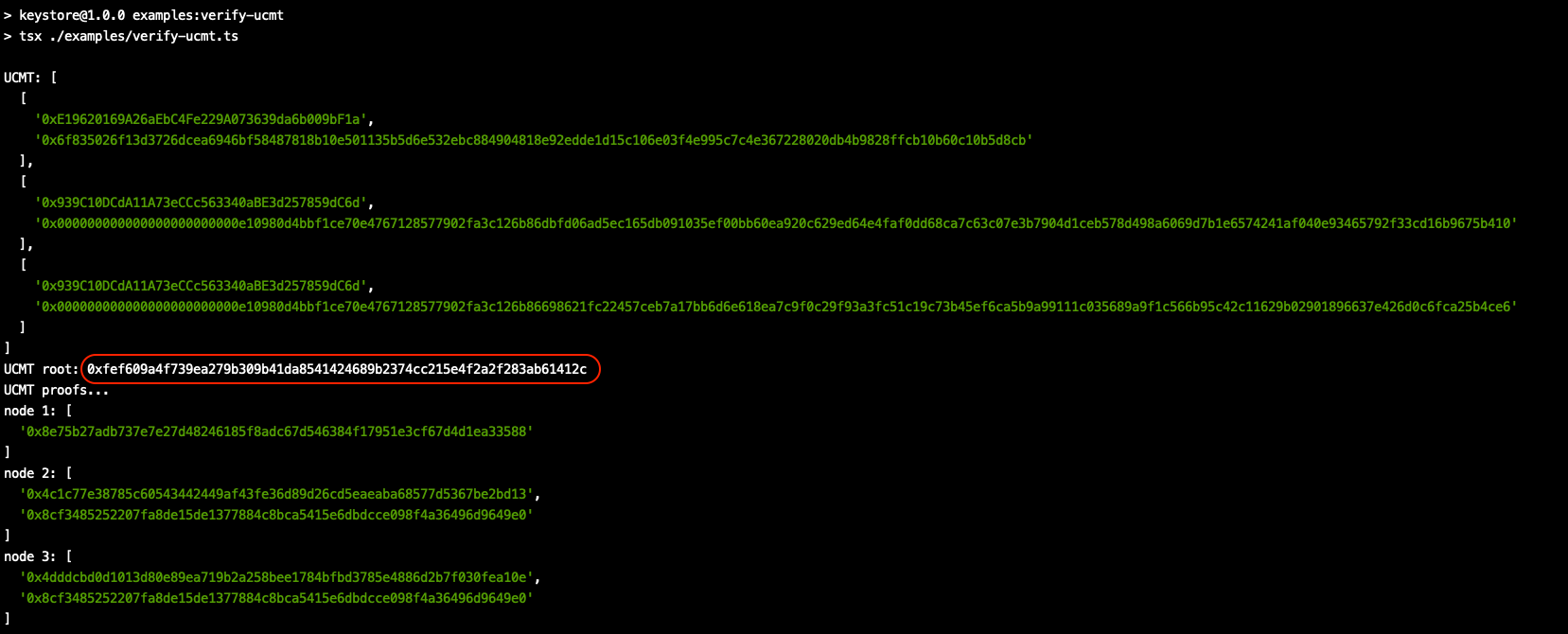
We can see that the calculated UCMT root exactly matches what we have in our JSON and what we see onchain. This is a strong cryptographic guarantee that your access configuration is shown in full and there are no malicious signers being hidden.
Smart account verification checklist
In summary, we can use the following steps to always verify that our Stackup smart accounts are non-custodial and configured as we intended.
Export onchain parameters from wallet settings.
Verify that v0.8 of the canonical EntryPoint is being used.
Verify that the canonical keystore factory is being used.
Run a
getSenderAddresssimulation on the EntryPoint with the factory address and data as the input.Verify generated address matches the exported account address value.
Verify that the canonical keystore is being used.
Use the
refHashand account address to query the keystore for the current root hash.Verify that the onchain root hash matches the latest value in the JSON export.
Calculate the root hash of the latest
userConfigurationMerkelTree.Verify that calculated root hash matches the expected value in our JSON.
This verification process can be quiet involved but is worth doing at least once to verify that your account is setup to be safe, secure, and non-custodial as you intended.